3 smart reasons to start using a VPN
The trending shift to remote and hybrid work is facing worrying technical and security challenges. One of many telecommuting concerns is ensuring safe network connections between sensitive corporate resources and remote workers. Interestingly, many entrepreneurs are turning to VPNs to solve this problem, as indicated by the considerable growth momentum of the VPN market over recent years.
VPNs enable businesses to meet modern workplace flexibility demands such as hybrid work and BYOD without compromising network security. Let’s discuss how you can apply VPN technologies to improve your organization’s network security and online privacy.
What is a VPN?
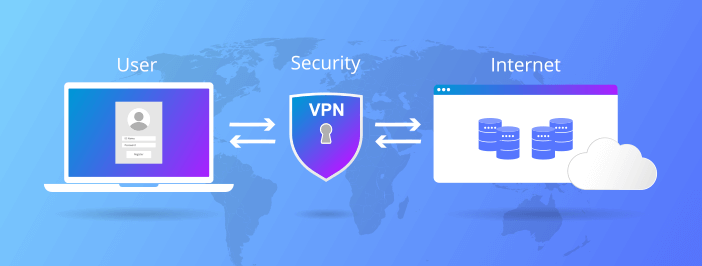
A VPN (Virtual Private Network) is an internet security service that creates an encrypted tunnel between an endpoint and a hosted server or service. VPNs can securely connect end-user devices such as smartphones, laptops, and workstations to a corporate intranet or the public internet.
The main goal of a VPN is to prevent risky exposure of the user’s web or intranet traffic on the open internet where snoopy threat actors, trackers, ISPs, and advertisers might be eavesdropping. A VPN essentially anonymizes its user’s web activities, location, and identity by encrypting end-to-end connections and data transfers through a proxy server.
Why you should use a VPN
When asked the reasons for using a VPN, most of the respondents in a survey cited online security and privacy. A good number also said they use VPNs for their jobs, when browsing on public Wi-Fi, to hide their online activities from search engines and ISPs, and bypass geo-censorship. All these are valid VPN uses. The question is: how do these apply in a business or workplace setting?
Protect your online privacy
According to the 2021 Norton Cyber Safety Insights Report, more than 75 percent of internet users are concerned about their online privacy. And many have taken actions, including using VPNs, to protect their personal information and online activities from prying eyes.
A breach in online privacy can expose sensitive personal or corporate information that cybercriminals can use to fabricate targeted cyberattacks, particularly social engineering scams. A VPN automatically encrypts and masks online connections and requests so that no sensitive information (click-through history, browser data, IP addresses, etc.) leaks into the wrong hands.
Secure connections on public Wi-Fi
Public Wi-Fi hotspots can be dangerous. For one, a threat actor can easily get between your device and the access point. So, instead of your online data, including credentials, emails, and personal details, going straight to the intended web service, it is sent to the hacker. Cybercriminals can also use unsecured Wi-Fi connections to distribute and install malware.
If you must connect to a public Wi-Fi hotspot, secure the connection with a VPN. The strong VPN encryption renders any intercepted data utterly useless to malicious eavesdroppers.
Access geo-blocked resources
Access to select websites, web services, and online content may be blocked or limited in some counties for social-political reasons. This blockage can be a big problem when working with a distributed remote workforce. The best way around geo-censorship is to tunnel the internet connection through a foreign VPN proxy server. Doing so makes your connection appear to come from a different county or region, conveniently bypassing any local geo-blocking.
A VPN is a consumer-level service distributed as a desktop app, smartphone app, or browser extension. Most VPN vendors also offer customizable business subscription packages for multiple clients and enterprise use cases. But even the best VPN does not guarantee 100% cybersecurity; privacy is just one of many facets of online security. Reach out to GB Tech to learn other ways to protect your data from cybercriminals by building a multi-layered security framework.